How Do U Know When to Use Which Gas Constant
The value of the gas constant R depends on the units used for pressure volume and temperature. The value of R in atm is constant.

Ideal Gas Law Physics Problems With Boltzmann S Constant Youtube
In physics the gas constant is defined as the product of pressure and volume.

. The odor may be due to sulfur in the flatus. The Gas Constant is the physical constant in the equation for the Ideal Gas Law. The R is also known as ideal gas constant or universal gas constant or molar constant.
You will choose the R value based off of the units for the known quantities in the problem. 123cp cV R. It is a gas constant per unit mass and it is different for different gases.
Characteristic Gas Constant R. The gas constant is a physical constant denoted by R and is expressed in terms of units of energy per temperature increment per mole. The ideal gas constant value ultimately depends on the unit of the quantities given in.
Heat flows into the gas just rapidly enough to keep the pressure constant at 165 x 105 Pa during the expansion. Rearranging the equation you can solve for R. 121 yields the relationship.
In SI units the real gas constant R is equal to 83145 Joulesmol K. The first approximation to all gases is a perfect gas which follows the relation that pressure volume nr atoms gas constant absolute temperature or PVNRT. Now N m is the equivalent to the joule which is the SI unit of energy.
How do you know which ideal gas constant to use. The SI unit of the ideal gas constant can be determined as. The specific gas constantR sometimes Rgas is notuniversal and its value depends on the specific gas being considered.
If we are calculating using the ideal gas equation PVnRT then we use the 08206 because we will we will be calculating either L atm mol or K. Experts consider passing gas up to 25 times a day to be normal. Where M is the molecular weight.
But the value of gas constant can be expressed using various units. Help me with this i really need it. However in using this constant on real gases it should be modified by applying characteristic gas constant other than universal gas constant.
V is the gas volume measurement m3. The specific gas constant R is thus the amount of mechanical work obtained by heating the unit mass of a gas through a unit temperature rise at constant pressure. You will have values or be looking for values for.
R represents the ideal gas constant. When the equation deals with mass the characteristic gas constant R is used. The ideal gas law is formed to explain the behavior of an ideal gas.
That is because none of the real gases behave as an ideal gas. A gas in a cylinder expands from a volume of 0110 m3 to 0320 m3. The letters are defined as follows.
To do this lets look at the units of the ideal. You will choose the R value based off of the units for the known quantities in the problem. The gas constant is 831 L-kPamol-K.
V - usually in liters T - Kelvin convert to Kelvin if given Celsius or Fahrenheit n moles P Pressure atm mmHg. T is the gas temperature measurement Kelvins. The SI unit of pressure is Pa or N m 2.
People who have problems with flatulence may feel they pass too much gas or that the flatus has an unpleasant odor. The behavior of an Ideal gas is described by the following equation PV nRT where P Pressure bar atmosphere Pa V Gaseous volume m 3 cm 3. It is also known as Ideal gas constant or molar gas constant or universal gas constant.
The gas constant is also found in the Nernst equation relating the reduction potential of a half-cell to the standard. Universal Gas Constant R The Universal Gas Constant R is common to all gases and its value is dependent on the units use to describe the rest of the ideal gas law equation. Substituting for p ρ in Eq.
Excess gas in the digestive tract that leads to passing gas is called flatulence. Its just a case of unit conversion. The gas that passes is called flatus.
The main difference between universal gas constant and characteristic. The ideal gas constant that you will use will depend on the units of the known quantities in the problem. The universal or R gas constant is widely used in thermodynamics lets look at the origin definition and values for different units of this widely used number in thermodynamics.
Denoted by R and expressed as energy per temperature increase per mole. The ideal gas constant that you will use will depend on the units of the known quantities in the problem. In SI units the universal gas.
The gas constant value is equivalent to Boltzmann constant but expressed as the pressure-volume product instead of energy per increment of temperature per. Youre going to look at your unit of pressure and if its in atmposheres youre going to use 0821 as your gas law constant. The ideal gas law equation is pV nRT.
P Pressure atm mmHg Torr kPa The key is usually pressure. Gas causes a number of digestive symptoms which can vary from person to person. Value of Ideal Gas Constant in SI unit At STP P 101 325 Pa T 27315 K the molar volume or volume per mole is 22414 10 3 m 3 mol 1.
R is defined as the universal gas constant divided by the molecular weight of the substance u R R M. R R say R barM. Prior to 2019 these were common values for the gas constant.
You will have an excess of gas and the. P is the gas pressure measurement Pa. The universal gas constant is used in the equation PVNRT a relation of a perfect gas.
P is pressure V is volume n is the number of moles and T is temperature. However if we express R in units of L atmmol K its value is 008206. N is the substance amount measurement moles.
The gas constant provides a proportional relationship between the kinetic energy of the molecules in a gas and the temperature of the gas. Stomach bloating or a feeling of fullness.

Boltzmann Constant Definition And Units
The Ideal Gas Law Equation Constant Chemtalk

Using The Ideal Gas Law To Calculate A Change In Volume Worked Example Video Khan Academy

Gas Constant Definition Formula Ideal Gas And Examples

Ideal Gas Law Equation Compressibility Of Natural Gas Chemistry
What Value Of R Gas Constant Should Be Used Quora

Ideal Gas Constant Easy Science Gas Constant Ideal Gas Law Chemical Changes
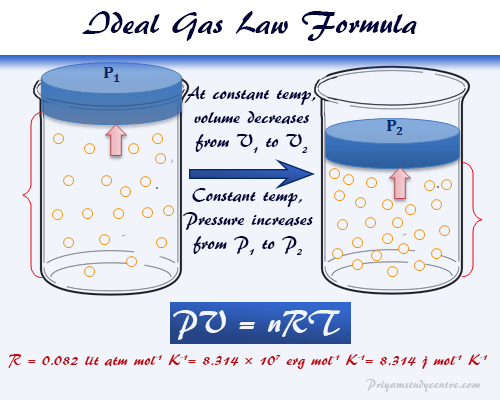
Ideal Gas Law Equation Formula Derivation Constant
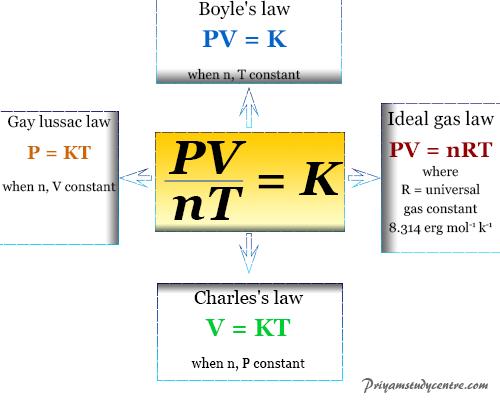
Gases Properties Formula Laws Derivation Graph

Question Video Recalling The Molar Volume Of A Gas At Rtp Nagwa

Ideal Gas Equation Its Derivation Ideal Gas Law Gas Constant Study Chemistry

Gas Laws Equations And Formulas Youtube

Using The Ideal Gas Law To Calculate Number Of Moles Worked Example Video Khan Academy

Ideal Gas Constant Definition Values And Units Chemistrygod

Imp Ideal Gas Law And Density Ideal Gas Law Physics And Mathematics Physics Formulas

Numerical Values Of The Gas Constant R In Various Units Chemistry Education Gas Constant Graphing
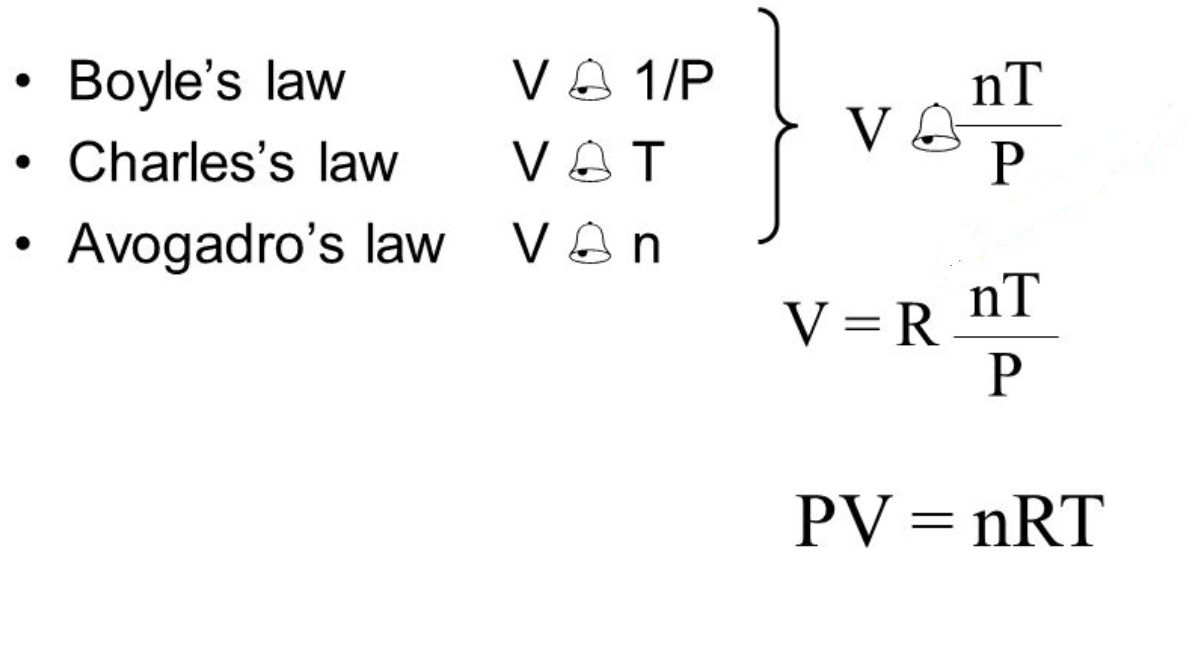


Comments
Post a Comment